
|
|
| . |
Motion Supervisor Object
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
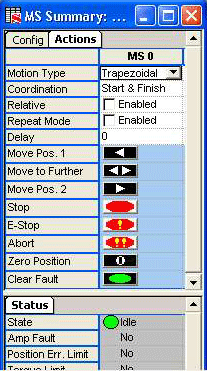
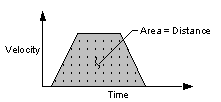
Motion Type – The motion type specifies the profile for the commanded motion trajectory.
Coordination – Determines the coordinated behavior when 2 or more axes are mapped to a motion supervisor:
Start – Axes start at the same time and each axis uses its specified motion trajectory parameters. Axes may finish at different times, depending on their specified trajectory parameters.
Finish - Axes finish at the same time and each axis uses its specified motion trajectory parameters. Axes may start at different time, depending on their specified trajectory parameters.
Start and Finish – Axes will start and finish at the same time. The trajectory parameters are scaled lowered based on the axis whose trajectory profile takes the longest time.
Delay – Time delay (in seconds) before execution of next move command. If operating in Repeat Mode, the delay will be applied to the beginning of each move segment.
Repeat Mode – [Enabled; (not enabled)] Repeats
programmed motion.
NOTE: Each repeated motion will be delayed by the Delay amount (see
description above on Delay).
![]()
Move Pos. 1 – Command each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor
to Position 1.
![]()
Move to Further – Command each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor
to either Position 1 or Position 2, whichever is further away.
![]()
Move Pos. 2 – Command each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor
to Position 2.
![]()
Stop – Stops movement of objects under control of current Motion
Supervisor within Stop time (seconds).
![]()
E-Stop – Emergency stop. Halts movement of objects under control
of current Motion Supervisor within E-Stop time (seconds) and leaves the
axes in an Error state.
NOTE: E-Stop does NOT disable closed-loop control and does not disable
the amp enable output(s).
![]()
Abort – Immediately stops movement of objects under control of current
Motion Supervisor, disables closed-loop control, and disables the amp
enable output(s), leaving the axes in an Error state.
![]()
CAUTION! Do not
use Abort when testing equipment which depends upon servos or stepper
motors to secure personnel or equipment (e.g., lifting cranes, elevators,
etc.). The Abort command disables servos and steppers and, in some circumstances,
may present a hazard to personnel or equipment due to sudden loss of power.
![]()
Zero Position – Sets the origin of the axis to the current actual
position and the command position to 0. The algorithm for setting the
origin is: new origin = current origin + actual position
![]()
Clear Fault – Clears the Motion Supervisor's error state and all
sub-object statuses. If you are having problems clearing the faults, it may be a result of improper axis mapping. Please see the Troubleshooting section.
Status fields are read-only:
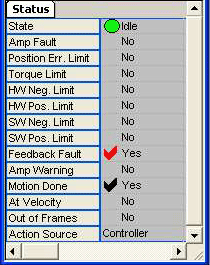
State – Current motion state. See Motion States table below.
|
State |
Description |
| Idle (State parameter). Awaiting a move command. | |
| In motion (State parameter). Performing a move command. | |
| Stopping. (State parameter). Motion has been commanded to stop. | |
| Moving when not commanded to
move. NOTE: This occurs when another application commands a move. |
|
| Initializing. | |
| Unknown state. | |
| Fault or limit detected. (See Event Status Flags below.) |
| A black checkmark indicates something positive. (ex: Motion Done, At Target) |
|
| A red checkmark indicates something potentially negative. (ex: error states, limits, amp fault, etc.) |
|
Error |
Flag |
Description |
| Amp[lifier] Fault |
|
Yes - Amplifier fault. |
| Position Error Limit |
|
Yes - Error between command and actual position exceeds user-defined limit. |
| Torque Limit | Yes – Torque limit has been exceeded. | |
| HW Neg. limit |
|
Yes - Hardware negative limit activated. |
| HW Pos. limit |
|
Yes - Hardware positive limit activated. |
| SW Neg. limit |
|
Yes - Software negative limit exceeded. |
| SW Pos. limit |
|
Yes - Software positive limit exceeded. |
| Feedback Fault |
|
Yes - Feedback fault detected. |
| Amp Warning |
|
Yes - Amp warning. |
| Motion Done |
|
Yes - Move command completed. |
| At Velocity |
|
Yes - Commanded velocity attained. |
| Out of Frames | Yes - Out of Frames. A Motion Done event was generated from a Motion Supervisor object. See MPIEventType. | |
| Action Source |
Controller | User |
Controller - Last action was commanded by the controller. User - Last action was commanded by you. See MPIActionSource. |
| | | Copyright © 2001-2009 Motion Engineering |