S-Curve Jerk Algorithm and
Attributes
|
|
Algorithm
|
|
|
The move type, MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE_JERK
supports a jerk-specified S-Curve accel/decel profile.
It is only available with custom firmware. To use this feature, you will need firmware with the Alternate Trajectory Creation Algorithm option enabled.
In the custom firmware, the Trapezoidal/S-Curve algorithm
is replaced with the S-Curve Jerk algorithm. In the
standard firmware, the S-Curve Jerk motion type is not
supported and if specified, the MPI will return a "profile
not supported" error. The S-Curve Jerk algorithm is
ideal for making final adjustments to a move during
the deceleration portion of the move and for making
smoother transitions from one motion to the next. Also,
the S-Curve Jerk algorithm makes it possible to exactly
specify the maximum accel/decel and jerk values.
|
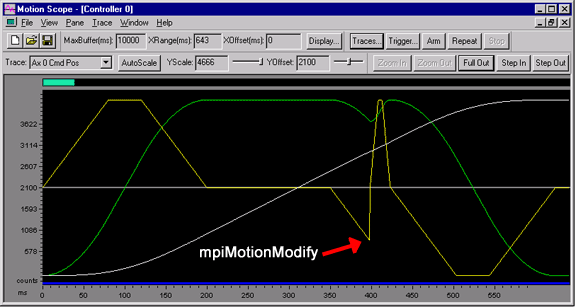
S-Curve Algorithm: Notice the mpiMotionModify
calculations assume the initial acceleration
value is zero, which causes an abrupt change in the
acceleration profile.
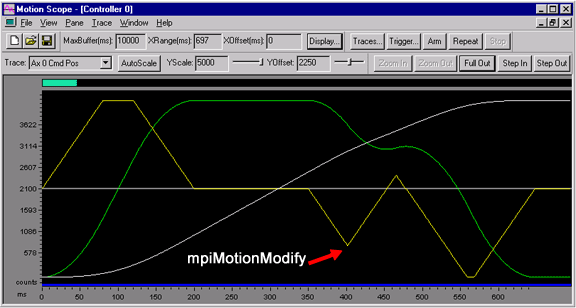
S-Curve Jerk Algorithm: Notice that the mpiMotionModify
calculations use the initial acceleration value, which
causes a much smoother transition in the acceleration
profile.
|
|
Parameters for jerk values
should range from a minimum of amax* amax / vmax (amax
is just reached when accelerating from 0 to vmax) and
a maximum of amax / sample period (amax is reached in
one sample period). In the S-Curve Jerk algorithm, changes
to the jerk will also change the time needed to complete
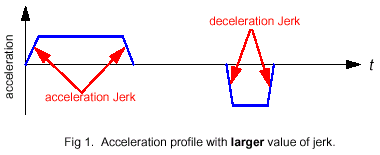
a motion. For example, a large value of jerk will have
a shorter time, but increase the "jerkiness" of the
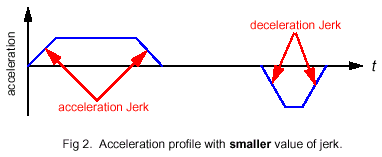
motion (see fig 1). Conversely, a small value of jerk
will have a longer time, but a much smoother motion
(see fig 2).
The S-Curve Jerk parameters, accelerationJerk
and decelerationJerk are located in the MPITrajectory{.}
structure. When these are non-zero, the acceleration
profile uses the specified jerk and acceleration to
ramp an axis(es) to constant velocity and then decelerate
to a stop. If accelerationJerk or decelerationJerk is
zero, the MPI will return a "parameter invalid" error.
For the move type, MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE,
the MPI calculates an appropriate jerk value based on
the specified velocity, acceleration, and jerkPercent.
The jerk value is computed according to the following
formula:
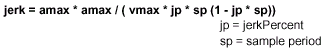
If jerkPercent is zero, the jerk value
is computed so that the maximum acceleration is reached
in one sample period. With the S-Curve algorithm, the
time for a move would not change as jerkPercent value
was varied. This is also true for this S-Curve algorithm,
as long as the move reaches maximum velocity. In short
moves, where maximum velocity is not reached, setting
jerkPercent to be small will result in a quicker move
than if you were to set jerkPercent to be large.
WARNING!
The same jerkPercent values may cause different profiles
with the special S-Curve Jerk algorithm than with the
standard S-Curve algorithm.
Custom Firmware Limitations (Option 2 & Option
21)
Due to controller memory limitations, the standard firmware
cannot fit the S-Curve Jerk algorithm. Thus, custom
firmware (Option 2 & Option 21) is required. To accomodate the
S-Curve Jerk algorithm, the following features are NOT
available with S-Curve Jerk firmware (Option 2 & Option 21):
- Pre-Filters· Compensation Tables
- Sinusoidal Commutation
- Stepper Motors
- Camming
- Back-up on path
- Metrics
Also, there are some limitations with the implementation
for the S-Curve Jerk algorithm:
- Multi-axis mpiMotionModify(.) must use the SYNC_START
attribute (and not use SYNC_END).
- The velocity, acceleration, deceleration, accelerationJerk,
decelerationJerk, or jerk Percent must be the same
for motion modify calls as for the original motion
start.
- The ratio of distances traveled for multi-axis moves
should not exceed 50,000.
- Multi-axis mpiMotionModify(.) should not be called
within the first 2 samples of a mpiMotionStart(.).
|
| |
|
Attributes
|
|
The new S_Curve algorithm behaves similarly to the
previous algorithm, except for its attributes.
MPIMotionAttrMaskDELAY
can now be used with any start motion, but never with
motion modify.
MPIMotionAttrMaskAPPEND
can be used with any motion, as long as it is not preceded
by a motion that has a final velocity.
MEIMotionAttrMaskNO_REVERSAL
returns a MPIMotionMessagePROFILE_ERROR if the given
specifications would result in a move with a reversal,
thereby preventing the move from being executed.
|
|
MPIMotionTypeTRAPEZOIDAL,
MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE, and MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE_JERK
MPIMotionAttrMaskRELATIVE,
when used with MPIMotionTypeTRAPEZOIDAL, MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE
and MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE_JERK means that the final position
is relative to the beginning position of the motion.
MEIMotionAttrMaskFINAL_VEL
can be used with MPIMotionTypeTRAPEZOIDAL, MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE
and MPIMotionTypeS_CURVE_JERK, but should be used with
caution as it may not be possible for the controller
to compute a trajectory to meet these criteria, which
would cause a MPIMotionMessagePROFILE_ERROR to be returned,
and the move to be ignored.
Multi-Axis Motion
Neither MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START
nor MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END
If neither MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START nor
MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END are specified, a single MPITrajectory{...}
may be specified for the resultant motion of multiple
axes on one motion supervisor. The motion of each axis
will be synchronized with the others on the motion supervisor.
The maximum velocity, acceleration, deceleration, and
jerk values of the first MPITrajectory structure will
be used for the global vector parameters. It will ignore
any other values supplied. This cannot be used with
MEIMotionAttrMaskFINAL_VEL.
MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START
or MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END but not both
If MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START or MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END
(but not both) is specified, each axis will move as
fast as possible and either start together, or stop
together. If motion is point-to-point and more than
one axis on the motion supervisor has a final velocity,
MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START or MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END
must be used. MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END cannot be used
with motion modify.
Both MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START
and MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END
With MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START and MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END,
the motion for each axis will be scaled so that the
motion of all axes will end at approximately the same
time. The time for this motion is based on the time
for the longest motion, so that the limits are not exceeded.
The axes will be scaled to start and stop together,
but the scaling may not be exact. Both MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START
and MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END cannot be used together
with MEIMotionAttrMaskFINAL_VEL.
MPIMotionTypeVELOCITY
MPIMotionTypeVELOCITY moves allow a final velocity
to be specified without a final point.
MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_START
and/or MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END
Neither is supported for this motion type. MPIMotionAttrMaskSYNC_END
cannot be used with motion modify.
MEIMotionAttrMaskFINAL_VEL
MEIMotionAttrMaskFINAL_VEL is not supported for this
motion type.
MPIMotionAttrMaskRELATIVE
MPIMotionAttrMaskRELATIVE, when used with MPIMotionTypeVELOCITY
or MPIMotionTypeVELOCITY_JERK, means that the final
velocity is relative to the velocity at the start of
the motion.
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
